Write Code That Read an Integer From a File Called Rawdata
Read Raw Information in SAS
In the last topic, we have learned how to merge datasets in SAS programming. Now, nosotros are going to acquire reading abilities of SAS, and too how to Read Raw Information from diverse kinds of files. We volition also learn to enter some special types of information values.
As we discussed earlier, a raw data file is a file that is temporarily stored by SAS for the execution of a program. In SAS, nosotros tin read raw information from many types of files like text, excel, CSV hierarchal, etc.
Reading Abilities of SAS
ane. Reading Infinite Separated Values
The data values, which are separated by the infinite, are oft called list. One or more spaces separate each value. If there are missing values, they should be pointed past the placeholder, such as dot (.) or total stop or period.
Annotation that a dot (.) is used to indicate a missing value for either numeric or character variables.
For Example:
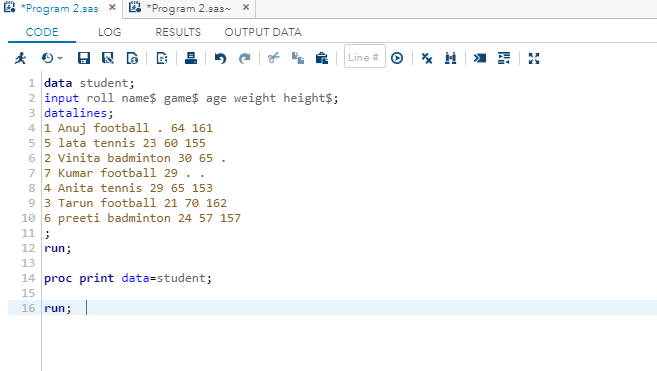
Output:
As you can see in the output, each value separated past space is creating a listing. Nosotros provided dot (.) on the place of missing values, and SAS is also reading it for missing values.
2. How to Enter Instream Information
We tin provide reading data to SAS in two ways, one when the data is besides big, so read it from an external file instead of typing, but when the data is as well pocket-size, then information technology is convenient to blazon the data in the SAS program instead of reading it from an external file. It is known as instream data. This is a quick way to enter data in SAS.
To enter this type of data, you volition need four basic types of statements:
- Data
- Input
- Cards or data lines
- A semicolon on a line
It is mandatory to have at least one space between data values, but nosotros can also give more than one space. It is essential for each variable to have a placeholder, even if the value is missing. A menstruation (.) works to indicate a missing value for both character and numerical variables entered in this way. In that location is no need to align the data exactly in the columns.
For Case:
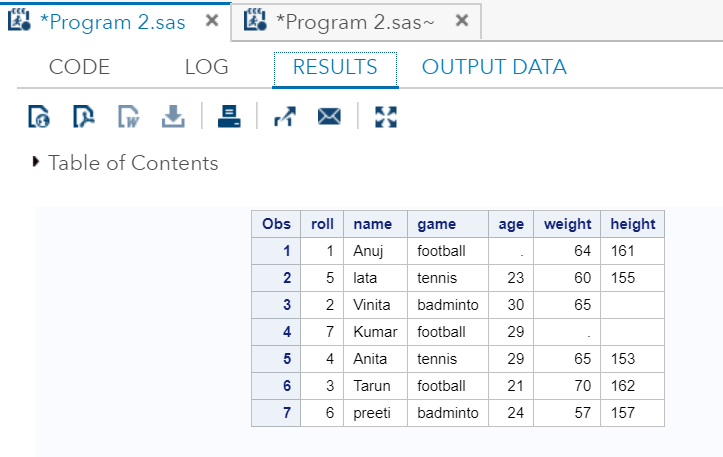
Output:
Y'all can see in the output, data have entered in a tabular form.
3. Enter information for Several Cases on The Aforementioned Line
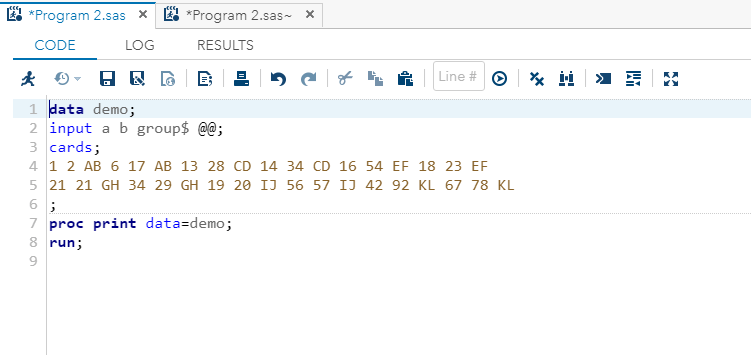
In SAS, we can utilise @@ to enter raw data on the same line for several cases.
For Example:
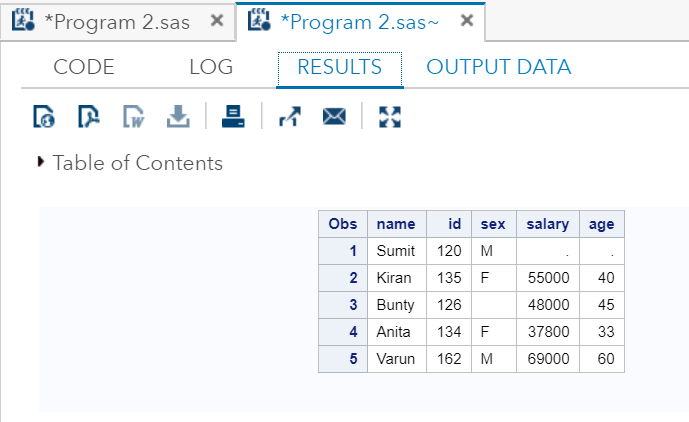
When you execute this code in SAS studio, will get the following output which shows that data take been entered:
Output:
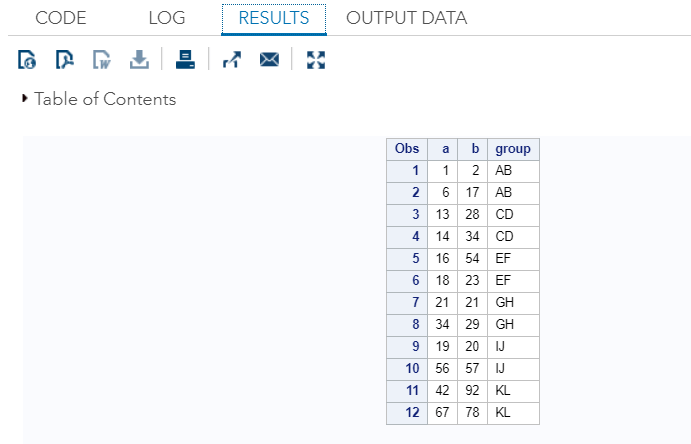
We can come across in the output, the data have been entered in several cases.
Reading data from External Files
In SAS, when the data is too large, so read it from an external file instead of typing. Nosotros can read data from many dissimilar sources such as exported from a database program, from a spreadsheet program or excel etc.
To do this, outset, brand certain that you should know the characteristics of the raw data file. You tin read and check raw data by using text editors or word processing programs.
For small size files, you tin can use Windows Notepad, and for large size files, you can utilise Microsoft Word or Give-and-take Perfect. Only brand certain that if you open up your raw data file with the discussion processing program, you can open the file that saved as text merely.
You will demand a codebook to read a raw data file. The codebook gives information about the contained data of the file. Some normally used raw data file types are:
- Space separated values: It contains data in the listing form.
- Comma-separated values: It typically comes from Excel with file extension .csv.
- Tab-separated values: Information technology is a kind of text file (.txt files) and come from a number of different applications, including Excel.
- Fixed-column data: Information technology is a kind of class which contains informative data.
For reading raw data from a file, the data step must include the post-obit 3 essential statements:
- Data
- Infile
- Input
Nosotros can add other statements in the information step to create new variables, recode variables and carry out information transformations.
Syntax to Read File
SAS data footstep is very uncomplicated to read raw data in SAS. The Information statement gives the name to create the data fix, and the infile statement indicates to read the raw data file.
For Case:
Y'all can encounter in the example, the test is a dataset created by DATA statement, and INFILE is used to read the raw data file, i.e., in. Input statement lists variables to read in the same sequence of the raw data file.
How to Command Reading Process?
In SAS, we can control data reading past using the loop. You cannot skip any variable at the get-go of the variable listing, but you can stop reading the variables before reaching the end of the list.
For Example:
As you lot can encounter in the example, you lot tin stop reading the index when it will cross 30.
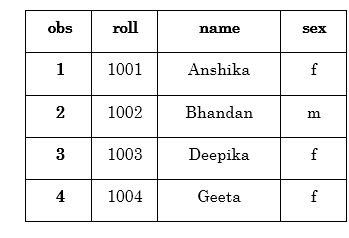
1. Reading from Text File (.txt files)
A file that contains data in the text format is called a text file. This blazon of files is generated by saving data with .txt extension. The data of these files is delimited by a space, merely there tin be various types of delimiters that are also handled by SAS. Let's understand through an example, how SAS reads the text file by using infile statement.
For Example:
Output:
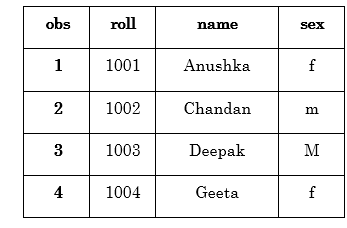
2. Reading from commas separated Values (.csv files)
The raw information values, which are separated by the comma or pipeline, are called CSV (Comma Separated Values). To read this type of files, use delimiter or short grade dlm in the infile statement.
For Example:
Where,
- delimiter = "," or dlm="," tells that commas are used in the raw data file to split up the values.
- firstobs: Information technology tells the line number (firstobs=ii) where from SAS can brainstorm reading the raw data file. This is the line where the actual values brainstorm.
- dsd: It indicates SAS to read consecutive commas equally missing values.
Output:
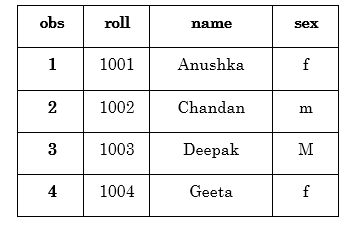
3. Reading from Excel File (.xls)
A file that contains information in the excel format is called excel file. These blazon of files are generated past saving data with .xls extension. Consider the following instance:
The higher up code is used to read data from excel file and gives data values in tabular class.
iv. Reading from Hierarchical Files
In the hierarchical files, the data is represented in a hierarchical format. These type of files incorporate observations; the number of records tin can vary observation to observation. Below is an case of a hierarchical file.
In the below file the details of each student under each branch are listed. The name of the branch will be considered as variable or column and record as observations or row. For the reading of the code, we utilize the below code in which nosotros can identify variable record with an IF and using the loop to get the observations.
For Example:
The above code is used to read data from excel file and gives information values in tabular form.
Write Code That Read an Integer From a File Called Rawdata
Source: https://www.javatpoint.com/read-raw-data-in-sas